导读 如果使用nestjs开发接口并部署之后,我们通常需要考虑到接口是否会被恶意盗刷消耗过多的资源,一个简单的方式就是限制在单位时间内的访问次数。
本文使用的库包版本如下:
库名 版本号
@nestjs/core 10.0.0
@nestjs/common 10.0.0
@nestjs/schedule 4.1.2
ioredis 5.4.2
本文的主要工作环境基于****Macbook Pro M1 MacOS 14.6.1 。
新建nestjs 项目 1 nest new nestjs-with-ip-limit -g
nestjs中的守卫Guard nestjs 提供了一种可以是否拦截请求的方式,守卫(Guard),我们可以通过实现 CanActive接口来完成,详细解释参考官方链接 。
自定义的一个 ip.guard.ts文件,用于最终实现我们的ip请求拦截。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 //ip.guard.ts import { Injectable, CanActivate, ExecutionContext } from '@nestjs/common'; import { Observable } from 'rxjs'; @Injectable() export class IpGuard implements CanActivate { canActivate( context: ExecutionContext, ): boolean | Promise<boolean> | Observable<boolean> { const request = context.switchToHttp().getRequest(); console.log(request.headers['origin'], request.headers); return request.headers['text'] != 'zoo' ? false : true; } }
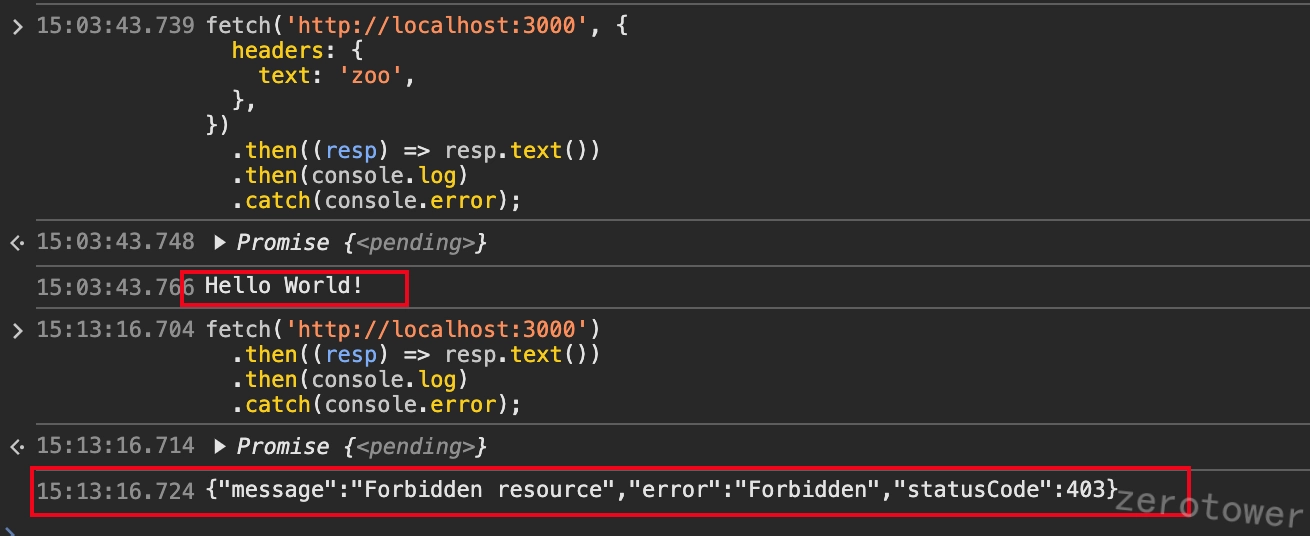
在示例中,我们增加当请求头没有text=zoo就拦截的逻辑,并直接在浏览器控制台中使用fetch测试:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 fetch('http://localhost:3000', { headers: { text: 'zoo', }, }) .then((resp) => resp.text()) .then(console.log) .catch(console.error);
可以看到,一旦守卫中返回了false,请求将报403请求错误。
Guard中获取IP 现在的问题就是如何在实现的 IpGuard中获取ip地址,可以通过context.switchToHttp().getRequest()获取请求对象来提取。
1 2 const request = context.switchToHttp().getRequest(); const ip = request.headers['x-forwarded-for'] || request.headers['x-real-ip'] || request.socket.remoteAddress || request.ip;
x-forwarded-for和x-real-ip的依据主要是我们很多网站可能使用代理的方式运行,尤其是nginx代理,如下所示。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 location ^~ /api { rewrite ^/api(.*) $1 break; # 重写规则,将/api之后的路径提取出来并去掉/api前缀 proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:6689; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; // 设置 X-Real-IP 头为客户端的真实 IP 地址。这对于后端服务识别客户端 IP 地址非常重要,特别是在请求经过多个代理的情况下 proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; // 设置 X-Forwarded-For 头为通过 proxy_add_x_forwarded_for 指令添加的信息。此头通常用于跟踪客户端 IP 地址以及任何之前的代理 IP 地址 proxy_set_header REMOTE-HOST $remote_addr; proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade; proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade"; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme; proxy_http_version 1.1; add_header X-Cache $upstream_cache_status; add_header Cache-Control no-cache; proxy_ssl_server_name off; }
ip存储 提取到ip地址后我们需要将其和请求数保存,并同时记录访问数(每次增加1),且在某段时间后清除,为此,我们需要引入redis。
为了后续更方便的使用,把redis封装为一个自建的module
1 nest g module redis --no-spec
新建 src/redis/redis.service.ts
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 import { Injectable } from '@nestjs/common'; import Client, { type RedisOptions } from 'ioredis'; @Injectable() export class RedisService extends Client { constructor(options: RedisOptions) { super(options); } }
在 redis.module.ts中加入代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 import { Module } from '@nestjs/common'; import { RedisOptions } from 'ioredis'; import { RedisService } from './redis.service'; @Module({}) export class RedisModule { static forRoot(optionts: RedisOptions) { return { module: RedisModule, providers: [ { provide: 'REDIS_OPTIONS', useValue: optionts, }, { provide: RedisService, useFactory: (options: RedisOptions) => { return new RedisService(options); }, inject: ['REDIS_OPTIONS'], }, ], exports: [RedisService], }; } }
在app.module.ts中使用
新建一个redis容器:
随后改造 ip.guard.ts文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 import { Injectable, CanActivate, ExecutionContext } from '@nestjs/common'; import { RedisService } from './redis/redis.service'; @Injectable() export class IpGuard implements CanActivate { constructor(private redisService: RedisService) {} async canActivate(context: ExecutionContext): Promise<boolean> { const request = context.switchToHttp().getRequest(); const ip = request.headers['x-forwarded-for'] || request.headers['x-real-ip'] || request.socket.remoteAddress || request.ip; const redis_key = 'limit_ip_' + ip; const data = await this.redisService.get(redis_key); const count = data ? parseInt(data) : 0; if (count >= 5) { return false; } await this.redisService.set( redis_key, data ? parseInt(data) + 1 : 1, 'EX', 60, ); return true; } }
每次接口访问时,都会先从redis里读取对应ip的访问次数,如果达到五次后,就返回false禁止接口应答,否则通过,并且该限制在一分钟内有效。
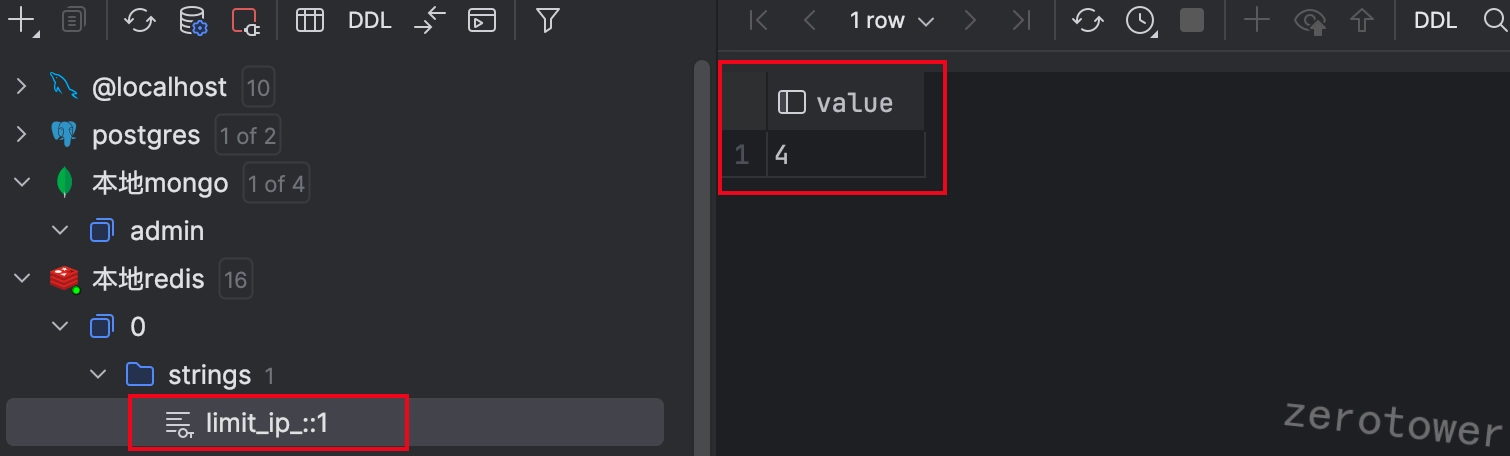
在浏览器请求 http://localhost:3000 ,刷新四次后,显示如下。::1是由于本地开发的缘故,如果有服务器可以在服务器上启动服务,本地测试。
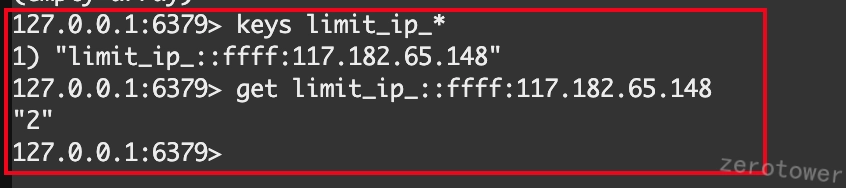
部署到服务器后显示:
补充 现在经常使用的一些AI工具,其免费计划每天都只有很少的额度,其也可以基于redis实现限流,不过是根据用户id来设置key值。除此之外,其每天到零点时还可以恢复额度。为此,可以在nestjs使用定时器在零点时删除所有的redis的ke y。
安装相关依赖
1 npm install @nestjs/schedule
注册定时任务模块
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 imports: [ RedisModule.forRoot({ host: 'localhost', port: 6378, db: 0, }), ScheduleModule.forRoot(), ],
在 app.service.ts加入代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 import { Injectable } from '@nestjs/common'; import { Cron, CronExpression } from '@nestjs/schedule'; import { RedisService } from './redis/redis.service'; @Injectable() export class AppService { constructor(private readonly redisService: RedisService) {} getHello(): string { return 'Hello World!'; } @Cron(CronExpression.EVERY_DAY_AT_1AM) async handleCron() { console.log('Called when the current time is 1AM'); //删除所有的redis keys: limit_ip_* await this.redisService.del('limit_ip_*'); } }
此外,也可以在定时任务中将相关的限流ip的计数同步到 MySQL,让相关逻辑更文档一些。